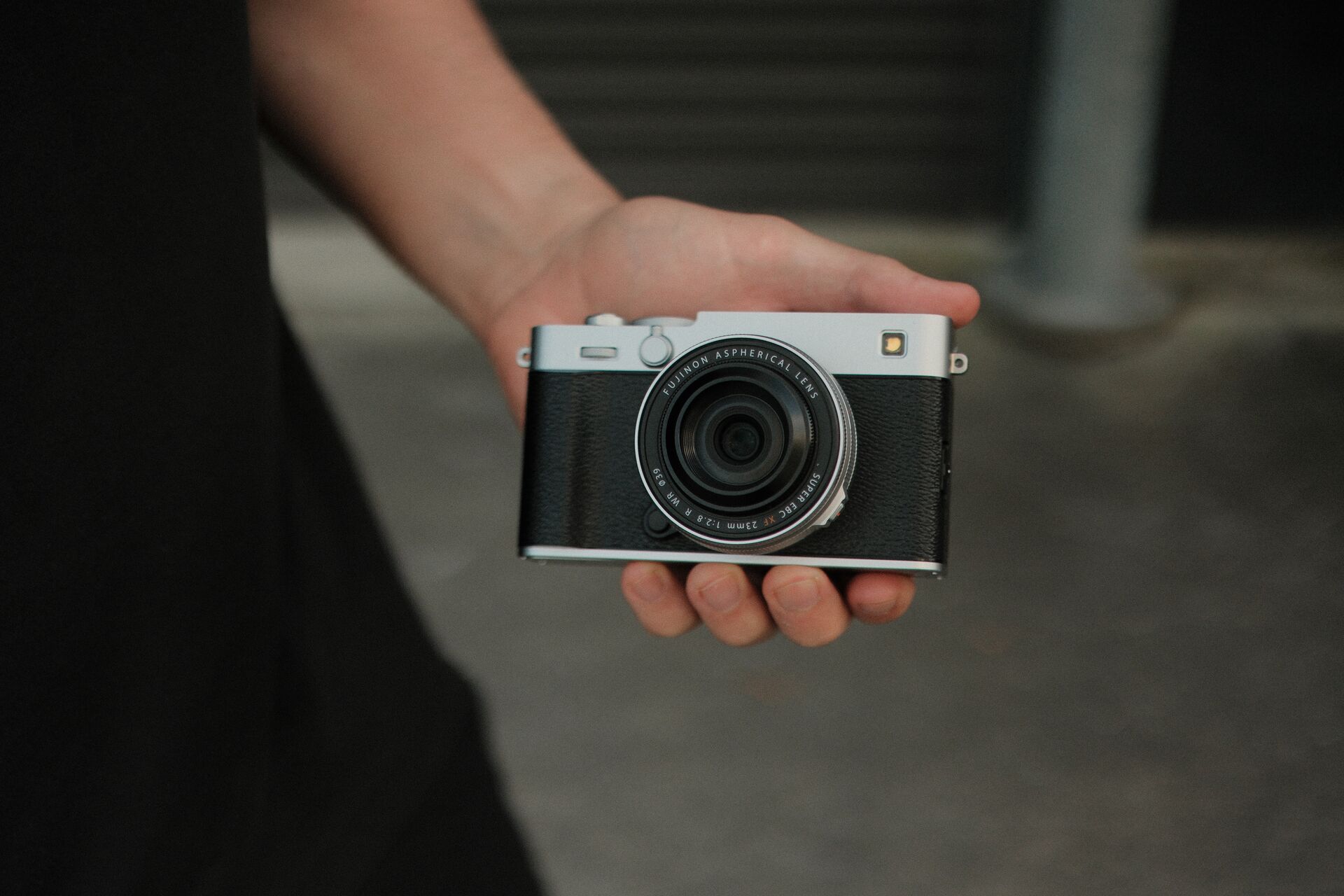
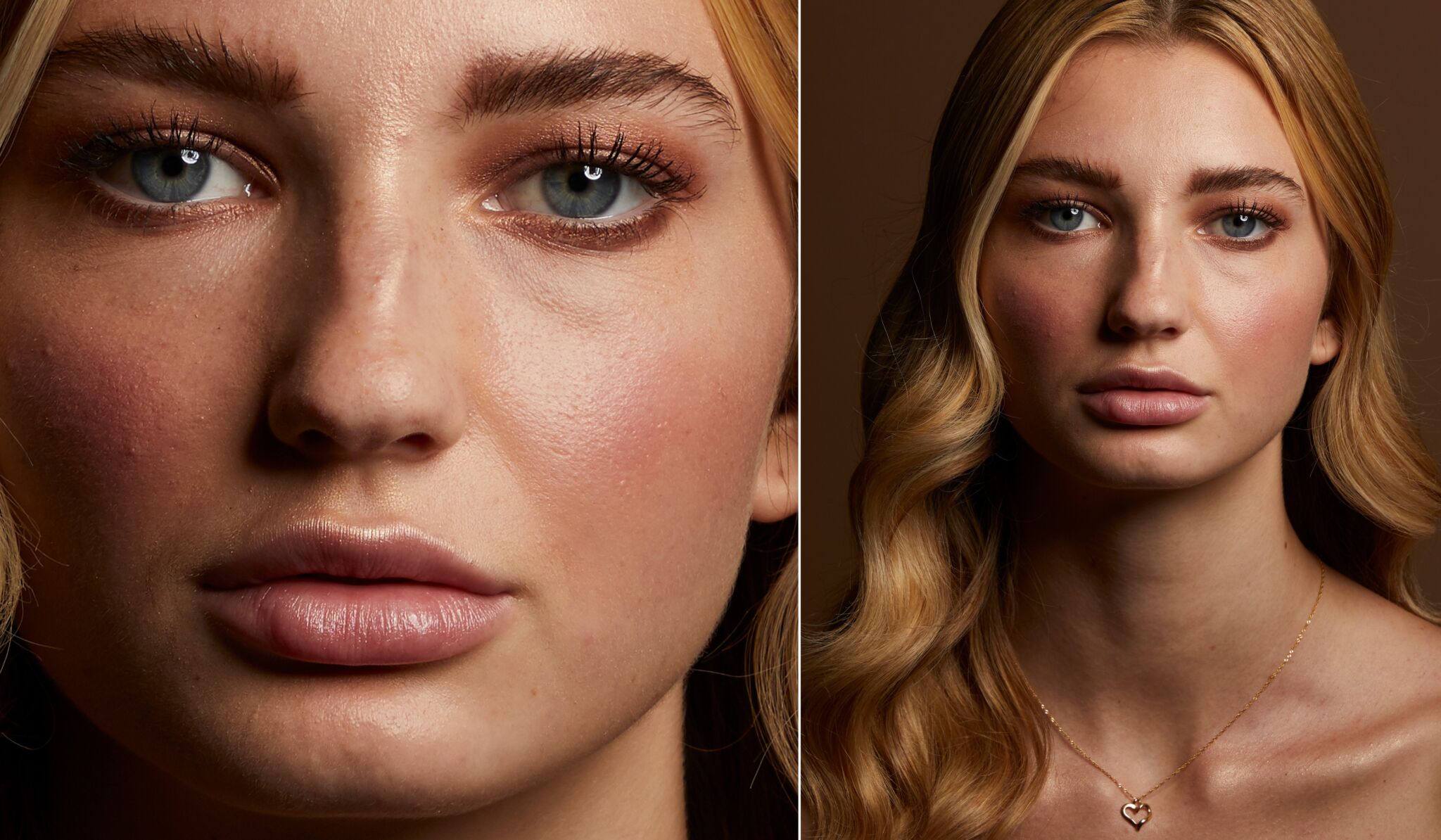
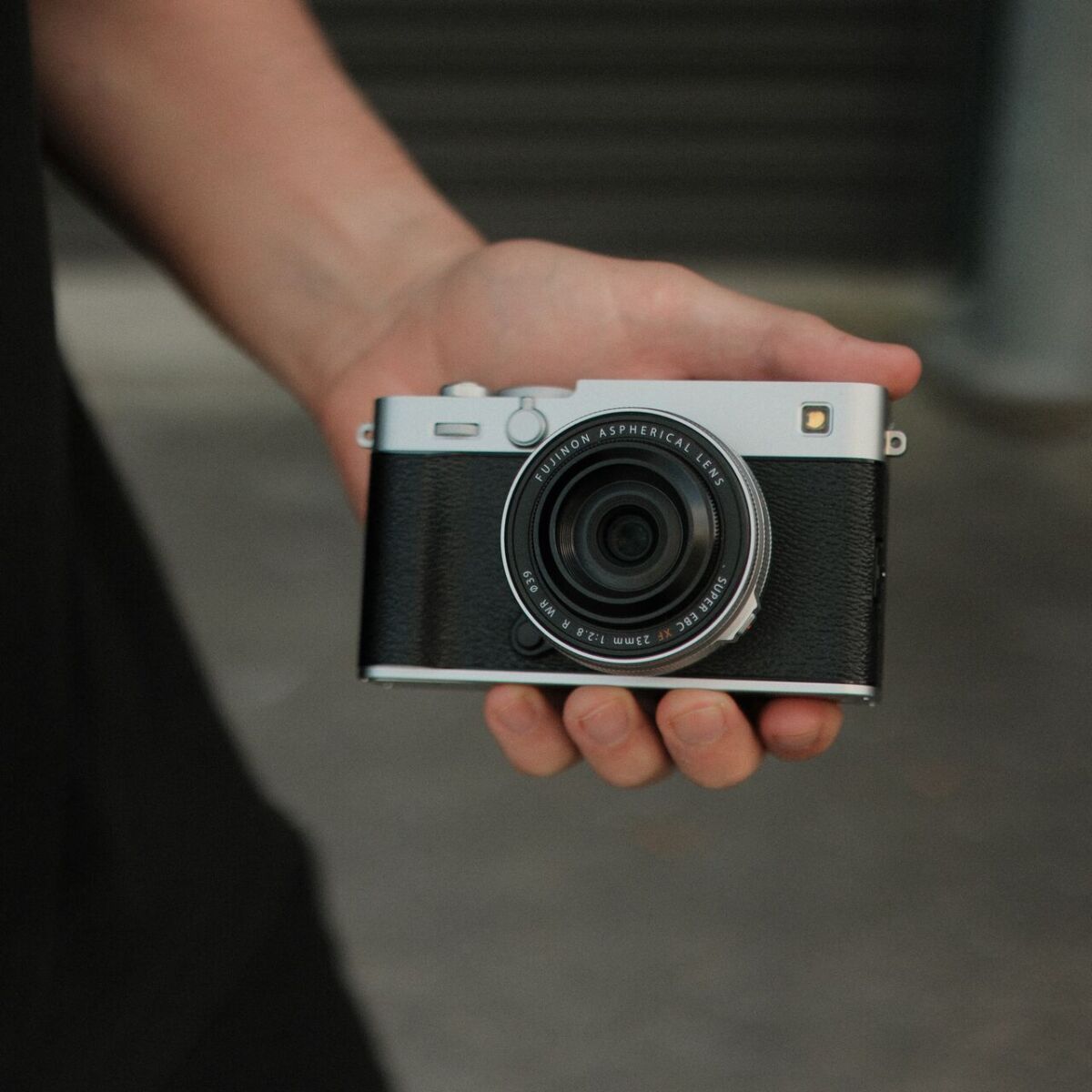
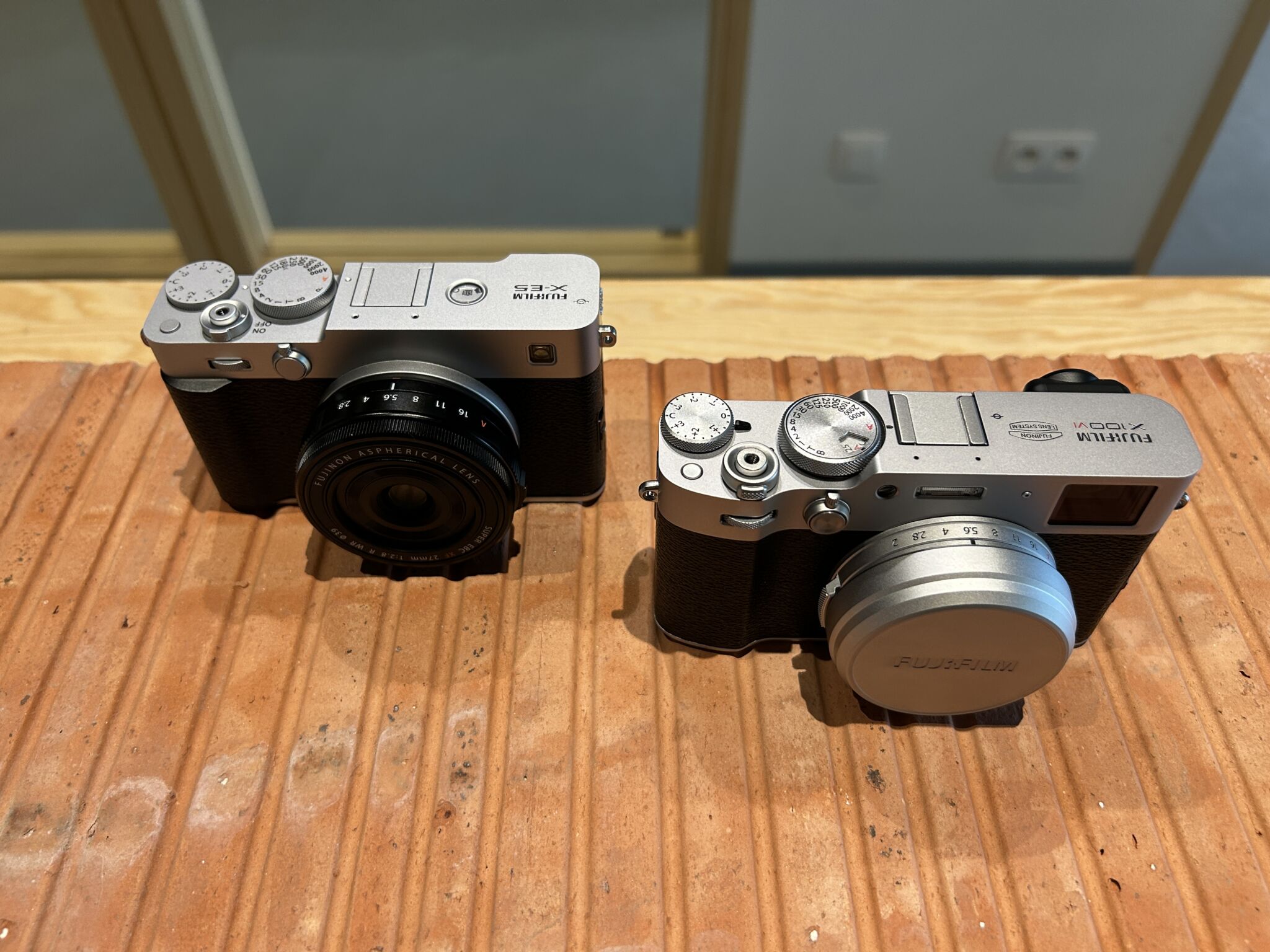
The Fujifilm X-E5, unveiled at X-Summit Shanghai, is a compact, lightweight APS-C hybrid body with a stabilized 40.2 MP sensor. Presented as the hybrid alternative to the X100VI, it lends itself perfectly to everyday photography, street photography and travel. In this article, we compare the X-E5 and X100VI to help you identify the differences and choose the model best suited to your needs.




























 Photo
Photo  Lighting
Lighting  Tripods & Grip
Tripods & Grip  Digital
Digital  Bags & Cases
Bags & Cases  Printing
Printing  Continous lights
Continous lights  Transmitters
Transmitters  Accessories & Parts
Accessories & Parts  Accessories tripods & grips
Accessories tripods & grips  Cables & Tether
Cables & Tether  Hub & Adaptaters
Hub & Adaptaters  Portable power stations
Portable power stations  Backpacks
Backpacks  Sling bags
Sling bags  Travel bag
Travel bag  Rolling bags
Rolling bags  Hard cases
Hard cases  Organizers & Pouches
Organizers & Pouches  Containers
Containers 








