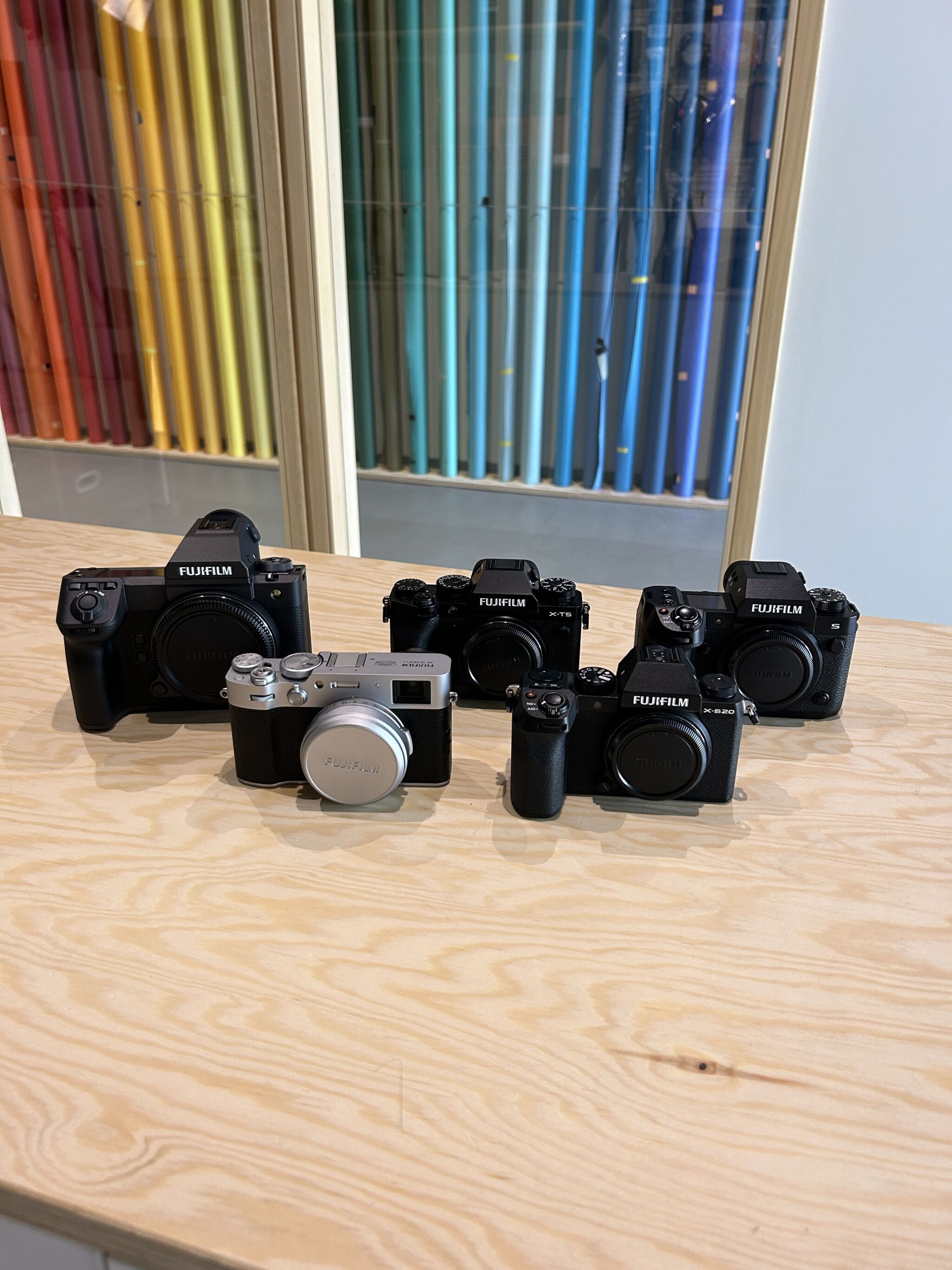
Our top 5 best Fujifilm cameras. Explore each camera’s detailed description and its strengths and weaknesses to help you determine which Fujifilm camera best suits your photographic needs.
Between SD, SDXC and SDUC cards, UHS-II and UHS-I standards, V30, V60 and V90 acronyms, it’s not always easy to understand the characteristics of SD memory cards.
In this article, we review the main features of the different SD cards.
We explain the different standards, acronyms and logos that exist, so that you can choose the memory card that best suits your photographic work.
Table of contents



1. The SD card, the photographer’s essential tool
The SD card is by far the best-known and most widely used memory card format.
Launched in 1999, this card format has established itself in many fields: photography, video, mobile consoles, action-cams, drones and smartphones.
SD memory cards are generally chosen for use in more or less high-end cameras, and have a dedicated slot in a good number of computers.
The characteristics of SD memory cards have evolved in recent years to the point of making the technical data sheet complex to understand and decipher. The certifications that were supposed to simplify understanding for consumers have actually had the opposite effect.
Let’s summarize the different characteristics of SD cards so that you can choose the one you need without any headaches.
2. SD memory card capacity
The first important feature to consider when choosing a memory card is its storage capacity.
There are four main categories: SD, SDHC, SDXC and SDUC.
|
Memory card type |
Capacity |
|
SD or SDSC (Secure Digital Standard Capacity) |
Up to 2 GB |
|
SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) |
Between 2 GB and 32 GB |
|
SDXC (Secure Digital eXtended Capacity) |
Between 32 GB and 2 TB |
|
SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity) |
Between 2 TB and 128 TB |
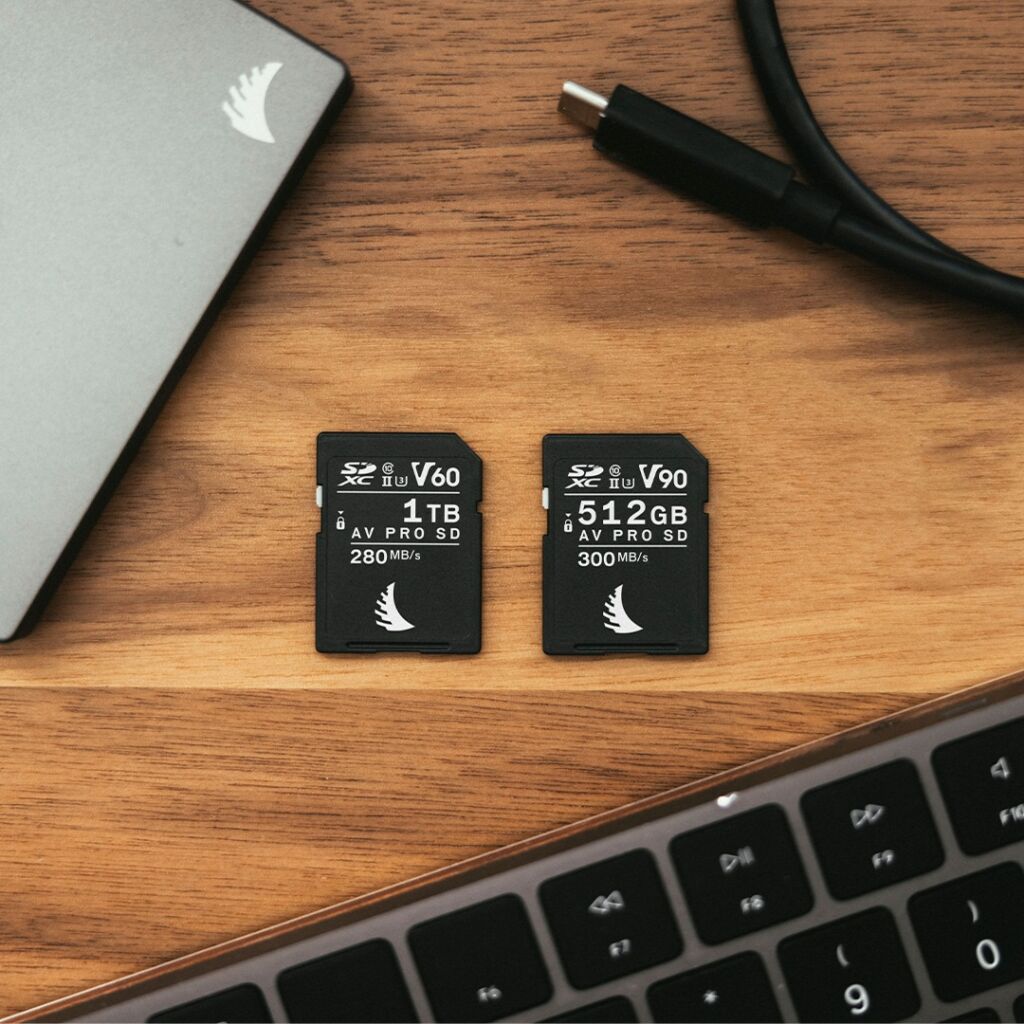
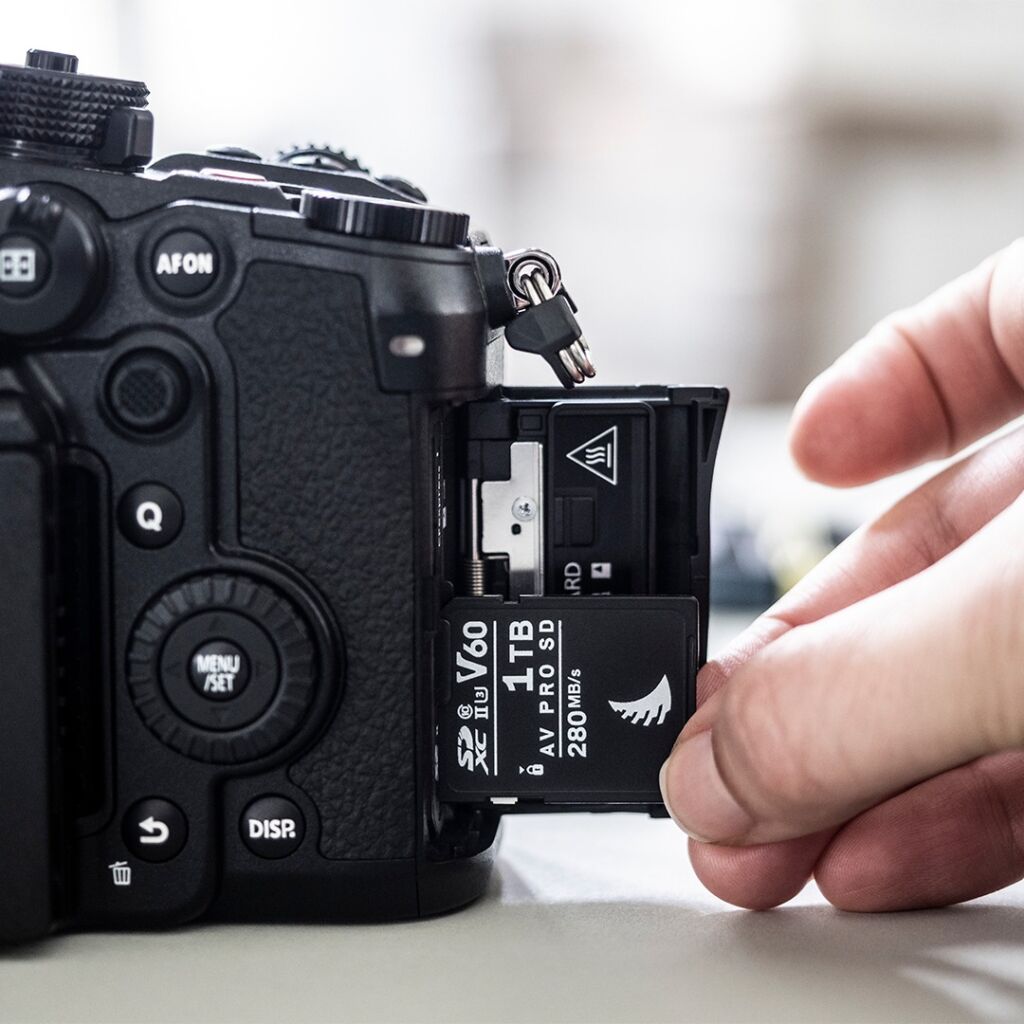


3. Reading speed
Another sign you’ll see on the SD card is I, II or III in Roman numerals.This sign indicates the reading speed of your SD card.
The SD card uses a communication interface called a “bus” to enable devices to read and write data to the card. This bus is responsible for the speed at which data is transferred between the card and the camera.
| Card symbol | Read speed |
| High Speed | Up to 25 MB/s |
| UHS-I (Ultra High Speed) | Up to 104 MB/s |
| UHS-II | Up to 312 MB/s |
| UHS-III | Up to 624 MB/s |
| SD EX | Up to 3940 MB/s |
4. Speed classes
In addition to the theoretical speeds permitted by the various buses and connectors used, such as UHS-I, UHS-II and UHS-III, SD cards also use three distinct symbols to represent their theoretical writing speed class: the speed class (class C), the high-speed class (class U) and the video speed class (class V).
- Class C2, C4, C6, C10: for respective minimum speeds of 2 MB/s, 4 MB/s, 6 MB/s, 10 MB/s.
- Class U1, U3: for minimum speeds of 10 MB/s and 30 MB/s respectively.
- Class V6, V10, V30, V60, V90: for minimum speeds of 6 MB/s, 10 MB/s, 30 MB/s, 60 MB/s, 90 MB/s respectively.
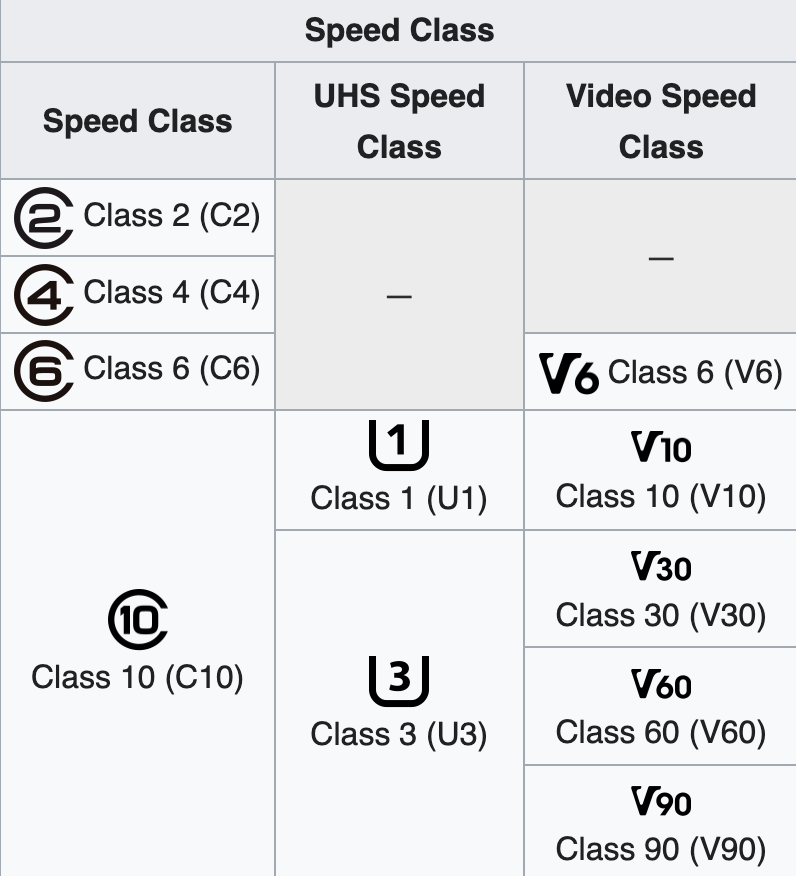
By definition, all V90 SD cards are therefore also U3 and C10. Similarly, V10 cards are necessarily U1 and C10. On the other hand, a C2 or C4 card cannot have any high-speed or video class, as its maximum write speed will be 4 or 6 MB/s.
Write speed is one of the parameters not to be overlooked when choosing your memory card.
Even if speed is not your priority, it’s always better to choose a fast memory card when opting for a large storage capacity. Otherwise, data transfer can take a long time.
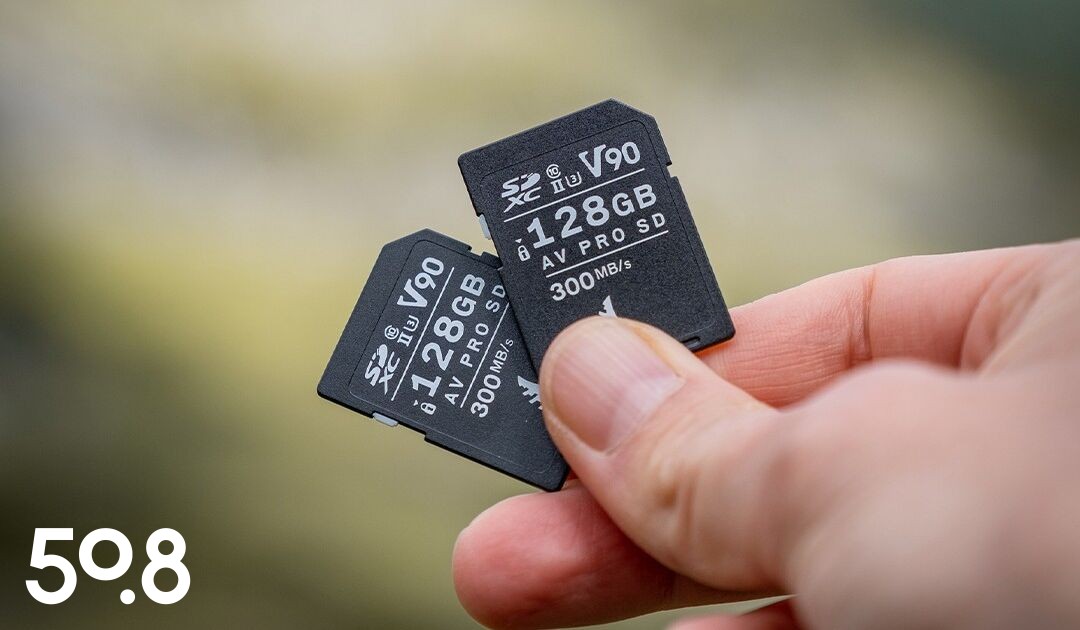
5. Example with the 64GB AV Pro V90 MK2 UHS-II SD memory card
Now let’s take Angelbird’s 64GB AV Pro V90 MK2 UHS-II SD card as an example, and decipher the various acronyms on it together.




 Photo
Photo  Lighting
Lighting  Tripods & Grip
Tripods & Grip  Digital
Digital  Bags & Cases
Bags & Cases  Printing
Printing  Continous lights
Continous lights  Transmitters
Transmitters  Accessories & Parts
Accessories & Parts  Accessories tripods & grips
Accessories tripods & grips  Cables & Tether
Cables & Tether  Hub & Adaptaters
Hub & Adaptaters  Portable power stations
Portable power stations  Sling bags
Sling bags  Rolling bags
Rolling bags  Hard cases
Hard cases  Organizers & Pouches
Organizers & Pouches 







